Yet another abbreviation from the IT sector. WebDAV stands for
- Web-based Distributed Authoring and Versioning.
What can you do with it? Shared editing, copying, moving files over the internet and much more is possible with this network protocol. This makes WebDAV highly suited for collaborative work from any location. As an illustrative example: If you use an online storage provider such as Strato HiDrive, MagentaCLOUD, Nextcloud, etc., then you are already working with WebDAV! In this article, we will briefly examine the history of the WebDAV protocol, the available options, its advantages and the problems it solves. Then we will put it into context with other, similar technologies.
Definition: What is WebDAV?
The WebDAV protocol came into being as an open internet standard in 1999. And it fulfilled a major need at the time. Back then, it was only possible to access and view websites, submit forms and call up links, WebDAV made it possible to collaboratively edit remote files. The main drivers of this protocol were and remain the work groups of the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force). The current request for comments is RFC 4918 from the year 2007. The WebDAV protocol also offers versioning. However, the latter feature is far from being implemented in all WebDAV servers.
What problem does the WebDAV protocol solve?
At that time, the web (that is, HTTP/HTML) was only in its infancy. Already in those days it was possible to access web pages as well as files via Hypertext Transfer Protocol – and even to edit them! The latter is just what Sir Tim Berners-Lee, the father of HTML and the World Wide Web, had in mind back in 1989-90. However, this option was quickly forgotten and fell to the wayside. Just as quickly, however, a working group was formed under the leadership of Jim Whitehead to develop the WebDAV protocol – and the rest is history. The goal was to enable “Distributed Authoring”. As such, WebDAV is based on HTTP/1.1 and is an extension of the HTTP protocol. Which later turned out to be a good decision.
What is a network protocol?
Network protocol means a fixed set of rules according to which the “communication” between two computers over the network works; here between WebDAV client and server.
How does the WebDAV protocol work?
As an RFC standard, WebDAV adds new methods to the HTTP verbs. These are crucial for file organization and management. Much of this revolves around simultaneous access to files, but it also concerns obtaining metadata on the requested resource.
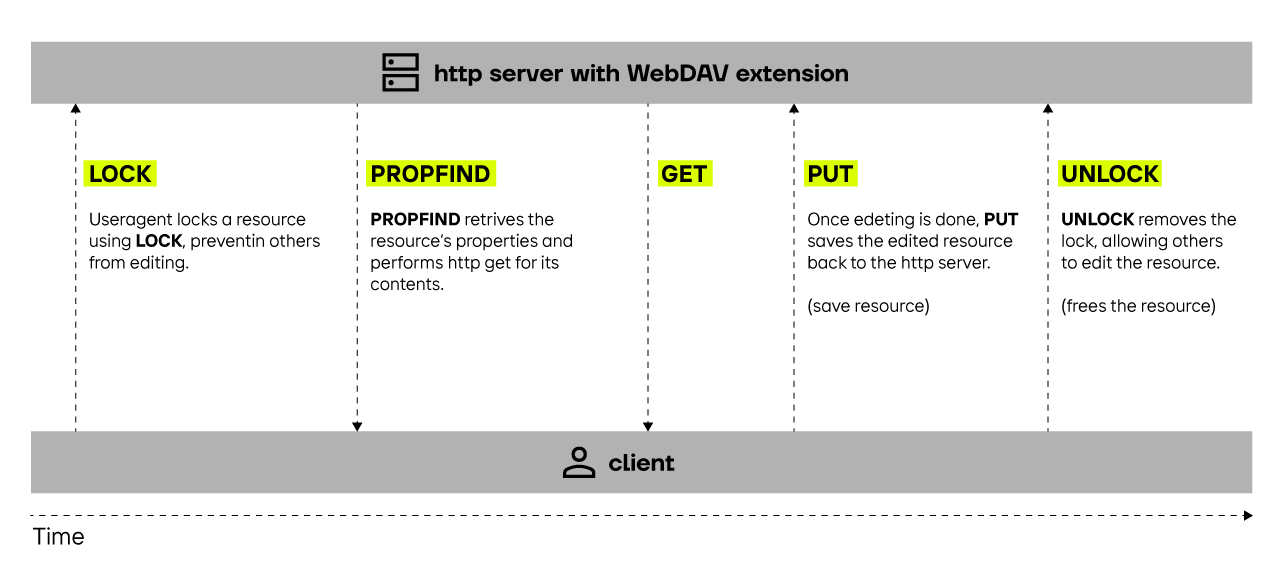
WebDAV methods for requests
Files, directories, etc. are called “resources” by the WeBDAV standard. These can be reached using the following WebDAV methods:
- PROPFIND: Retrieves properties defined for the resource identified by the request URI
- PROPPATCH: Can update and change these properties of the resource
- COPY: Copies files and directories
- MOVE: Moves these resources
- MKCOL: This can be used to create collections of resources (files and directories, etc.)
- DELETE: Enables deletion
- LOCK: Locks a WebDAV resource, e.g. while another user is editing the file
- UNLOCK: When the user finishes working on the file, this WebDAV method is used to share the resource
These WebDAV methods allow you to manage files and folders on a WebDAV server. Properties can be read, files can be locked, downloaded and uploaded, copied, moved and deleted.
Advantages of the WebDAV protocol
The client and server must both support WebDAV, of course. Since this protocol has been established over the last two decades and is now available platform-independently, many servers (Apache, Microsoft IIS, Nginx, etc.) speak and understand the WebDAV protocol. The same applies to operating systems (Linux, *BSD, MacOS, Microsoft Windows) as well as web browsers (via add-ons).
Moreover, no additional software is needed to use the WebDAV protocol. This is the big, decisive advantage of WebDAV. The protocol ranks among the platform-independent protocols – a true network protocol. On the client side, files and directories can be displayed either in the file browser (Explorer, Finder, etc.), in the web browser or in a WebDAV client. The directories and files are then displayed in the usual style as directory structures and the files they contain. These can be conveniently opened, edited, saved or deleted in Windows, MacOS or Linux – but with two further advantages:
- This transfer protocol allows you to access files on a remote server. For the user, directories and files present themselves as if they were stored locally. So there is no need for tedious downloading, editing, caching or uploading, at least that’s how it appears to the user. This makes WebDAV one of the ideal protocols for distributed, shared collaboration via cloud storage.
- Another important advantage: WebDAV uses port 80 or 443. These ports belong to HTTP and HTTPS, respectively. Blocked ports are therefore not to be expected. This means a free ride for applications on their way to the WebDAV server and no blocking by firewalls.
Are there alternatives to WebDAV?
Of course, because many roads lead to Rome. WebDAV is therefore just one option among many others for accessing cloud files. There are also FTPs (File Transfer Protocol, 1985), SFTPs (Secure File Transfer Protocol) and SSH (Secure Shell). However, compared to the WebDAV protocol, the aforementioned protocols and their associated client software do not offer the same high level of convenience. They also do not support collaborative editing or versioning. In contrast, SharePoint, Microsoft 365 or SSHFS (Secure SHell File System) can be used much more conveniently, depending on the application.
GDPR-compliant archiving – with easy WebDAV for SAP ILM
There are good reasons why WebDAV plays an important role in the context of information lifecycle management (ILM) and the GDPR. As an add-on to SAP ILM, easy WebDAV for SAP ILM provides ILM-capable storage for archive data and archive documents in easy archive. The underlying blocking and deletion concept enables the following functions:
- Define and manage retention policies
- Lock and delete data and documents
Now you can confidently face the extensive requirements for the mandatory implementation of the GDPR without worries. Here you can find detailed information about easy WebDAV for SAP ILM.


