SAP® ILM for GDPR
compliant data archiving
A uniform regulation for the protection of personal data has applied throughout the European Union: the EU General Data Protection Regulation. Companies in particular have had to deal intensively with this subject and still must if they haven’t already. This especially affects companies whose focus is on digitised business processes.
Information lifecycle management – always GDPR-compliant
The GDPR obliges companies to ensure that personal data is only used within narrow limits and deleted after certain periods across all processes. In concrete terms, this means you have to precisely define which employee in a process may have which access to certain personal data and for how long.
The second challenge in complying with GDPR relates to organizing the right to information that every customer has towards a company according to article 15 GDPR. Pursuant to this provision, an organization must disclose to a customer all personal data and metadata stored about the data subject if such information is requested.
Finally, the third challenge in implementing the GDPR is that companies must of course continue to comply with statutory retention periods for a wide variety of documents when handling personal data, such as those arising from tax, commercial or HR law.
The good news for businesses is that SAP® provides a solution in its ERP system with Information Lifecycle Management (SAP ILM), supporting organizations in this new data challenge. In this blog post, we’ll show you how best to proceed so you can move ahead confidently when it comes to all things GDPR.
Do you use easy archive in combination with an SAP ERP system – and are therefore required to archive in compliance with the GDPR? Then your search is at an end. easy has the right interface between easy Archive and the leading SAP ERP system: easy WebDAV for ILM. Do you want to know how easy WebDAV for SAP ILM works?
As a result, the customer must implement technical measures that meet the requirements of deleting and / or blocking such personal data. These technical and organizational measures (TOM) specifically include the implementation of SAP Information Lifecycle Management – in short: SAP ILM.
With the creation of a comprehensive blocking and deletion concept, the definition of a valid lifecycle management of data and documents and the use of SAP ILM, the company receives the ability to meet the requirements for the mandatory implementation of the GDPR. By doing so, fines for specific violations of data protection are permanently avoided, and financial risks are minimized. Furthermore, the company obtains an effective lifecycle management of its data and can thus meet the requirements of digitization much more robustly.
Many companies try to outsource responsibility for SAP ILM to one area or person in the company so that the process remains as lean and clear as possible. In our experience, however, this approach is not effective because the topic is too complex for this and affects too many areas in the business. For this reason, we recommend you first ask which departments are affected by GDPR requirements and involve one employee from each of these departments in the project planning. The data protection officer should play a special role in this.
In the second step, those involved in their departments must identify all relevant documents, data, programs and processes. The decisive question here is: where is data collected for which you have to devise deletion or blocking rules? For this purpose, it’s helpful to group the data into different categories such as customer data, usage data and contact data.
In the third step, you have to collect the correct retention periods and deletion requirements for all data. To do this, you should describe as comprehensively as possible which retention obligations apply and in which departments and processes data and documents are handled in the company.
In the fourth step, you need to summarize and structure all the information in order to generate concrete blocking and deletion concepts. To do this, you may find it helpful to follow the trail of data through the entire company with the data protection officer and employees from the departments concerned and to record it in detail. The ultimate goal is to have a record of all the different media that contain personal data. For example, these include invoices, database entries, paper receipts, certificates, order confirmations, delivery bills, cover letters or resumes.
The actual blocking and deletion concept can be very well created in tabular form. It should specify for each object which information should be blocked or deleted in which process, which blocking and deletion periods apply, and on what legal basis they’re founded.
Once you’ve defined the project scope and determined what is captured and how, you can activate SAP ILM in your SAP system. You then finalize the project by setting up an ILM policy for each relevant object. This means that you use the policy in SAP ILM to define exactly which attributes apply to archiving and deletion for each object. Predefined policy categories are used to determine which retention and residence rules, e.g. to comply with legal hold requirements, apply to an object in the database.
Finally, create the authorization concept. It should be created as a matrix and serves to link employee groups and data. The authorization concept defines who is allowed to access what and when in the system. For this purpose, fixed access rules, processes and roles are defined, which make the handling of data GDPR-compliant.
Let yourself be guided by the “need-to-know” principle, which specifies the principle of purpose limitation when handling personal data in article 32 GDPR under the heading “Security of processing”. It states that each employee in the company may only access the data that they absolutely need for their project. A written or digital document is created from the authorization concept after implementation, as required by the legal obligation to produce proof in the GDPR.
EASY WebDAV for SAP ILM the bidirectional interface between SAP and EASY Archive
SAP ILM is already included in the standard SAP package and offers companies the option of creating rules to archive and delete data according to certain specifications. However, implementing SAP ILM is not done by simply activating the feature in the software and setting it up in an automated basic variant.
Rather, SAP ILM requires incredibly detailed implementation to ensure that all processes in your company are really covered while complying with the entire legal framework. That’s why it’s essential to implement every SAP ILM project in a very targeted manner. There are two stages in the process:
- The preparation phase, in which the necessary information for later implementation is gathered and summarized in concepts,
- The implementation phase, in which you set up and implement detailed blocking, deletion and authorization concepts in SAP ILM.
Alongside developing blocking and deletion concepts, you should also analyze your IT infrastructure from a GDPR perspective. The aim here is to find out:
- Which systems supply data to the ERP,
- Which interfaces are created in the process,
- Where and in which form – from a technical perspective – data can be found and
- What other dependencies may exist with other systems.
The purpose of this measure is to gain control over the entire data flow that is relevant for SAP ILM. You can find further requirements for the smooth operation of easy WebDAV for ILM in the following overview.
- A configured SAP ILM system
- easy for SAP
- easy archive
- easy WebDAV for ILM as an extension module for easy for SAP
SAP ILM – a detailed look at Information Lifecycle Management:
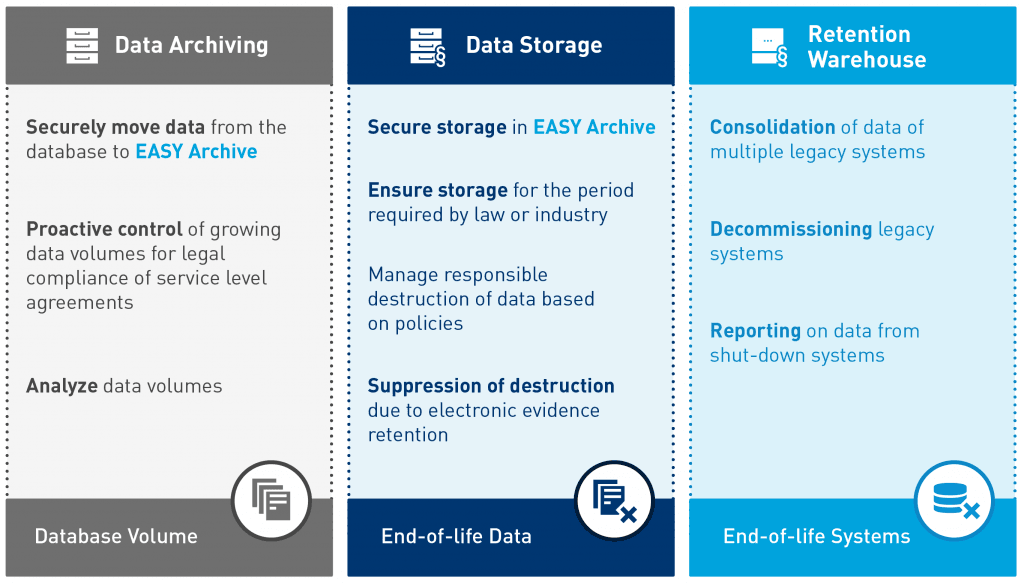
All personal data have a lifecycle. SAP Net Weaver ILM (SAP NetWeaver Information Lifecycle Management) adds the ability to manage the lifecycle more productively and to control archived data and documents based on rules to the standard SAP delivery. SAP NetWeaver ILM uses expanded data archiving functions specific to SAP ILM.
With the use of easy WebDAV for ILM as an extension to SAP ILM, you gain the ability to conform with all comprehensive requirements for the mandatory implementation of the GDPR. easy WebDAV for ILM particularly meets the requirement for providing ILM-capable storage for archive data and archive documents. The following diagram illustrates the interaction of SAP ILM, easy WebDAV for ILM and easy archive.
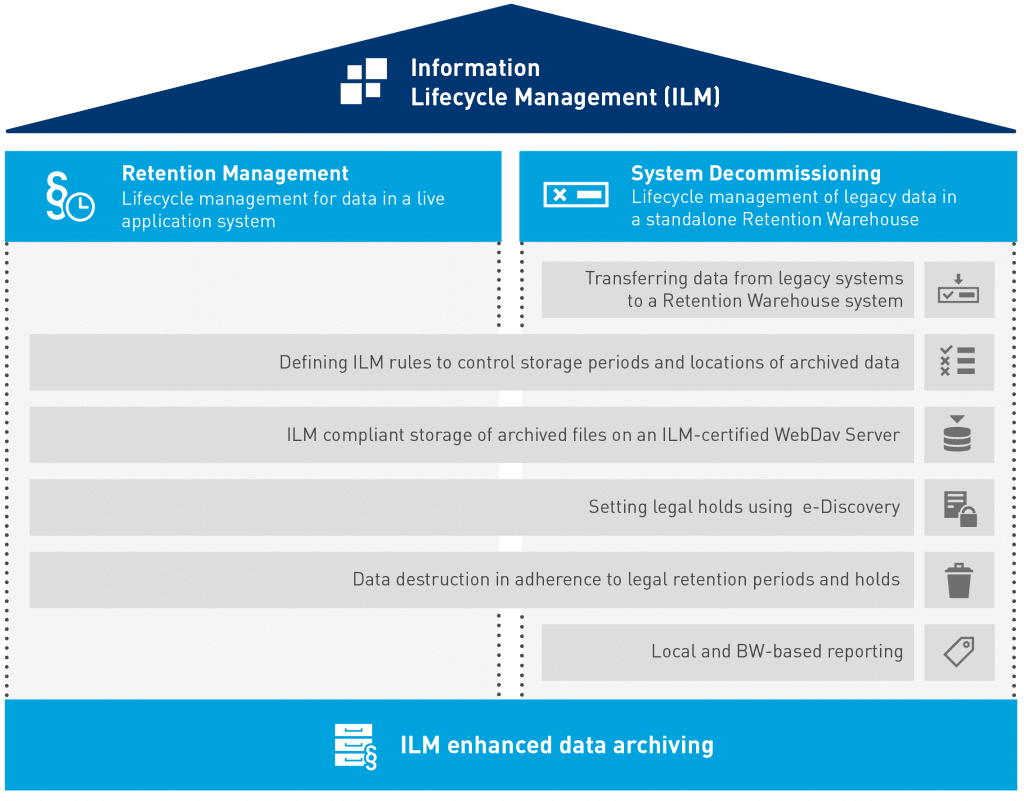
easy WebDAV for SAP ILM includes the ILM-capable document archive storage via an easy WebDAV server and meets all the requirements of SAP for ILM-capable storage:
- Definition and management of retention policies
- Storage and retention of information in file systems
- Simplified blocking and deletion of data and documents (as a subfunction of the information retention management scenario (IRM) of SAP ILM)
- Elimination of data or documents from the archive or a database
- Establishment of extraordinary retention periods, including the support of preservation of evidence procedures
S/4HANA
Cost-optimized data archiving before switching to S/4HANA
Moving to the new S/4HANA system requires enormous resources. Everything needs to be well planned: A detailed roadmap and a clear migration path requires several man-hours. After all your efforts, you will achieve a successful transition to the new S/4HANA system. S/4 is high performing because it resides in an in-memory DB. This is where the difficulty lies. S/4HANA will certainly perform better than any other SAP system has before. But this is exactly where SAP keeps silent: What costs will you have to deal with? One thing is clear, with the migration to S/4HANA, you can expect a gigabyte-based volume license. Every gigabyte in the HANA-DB costs money. At this point, a well-thought-out strategy can significantly reduce costs.
Plan your transfer cost effectively
- Data Cleansing: Determine data records that are to be archived from your SAP production system.
- Data Archiving: Archive the determined data records in a compliant archive.
- Reduce costs: Save cash with your archiving strategy when moving to S/4HANA.
