BLOG
How to Optimize Your Company-Wide SAP Master Data Management
How do you optimise, streamline and accelerate your SAP Master Data Management (MDM) and why is it so important? Discover how correct master data forms the basis for digital processes, S/4HANA and IoT. Learn how to calculate ROI, implement data governance, avoid errors and realise SAP’s potential.
Companies that display their business processes on the basis of ERP systems such as SAP should therefore not underestimate the effort that is needed to maintain their master data. Incorrect or outdated data causes problems when it comes to processing SAP applications – and in the worst case, can bring your business processes to a complete standstill. Every company that displays its business processes in SAP should address the following questions:
- SAP master data workflow: Have you established a process whereby you regularly and ideally automatically check your master data for errors and duplicates?
- SAP master data governance: Are the responsibilities for master data maintenance clearly defined in your organization and do all the employees involved know what to do and when?
- SAP master data management best practices: Do you rely on established standards for your company-wide SAP master data management and thereby lay the foundation for the successful digitalization of your business processes?
In this blog post you’ll learn why you should think about your company-wide master data management (MDM) processes and how to optimize, streamline and accelerate your SAP MDM.
As the volume of data explodes, MDM has developed into one of the most exciting areas in the global IT market. We expect MDM solutions to generate annual growth rates of more than 15 percent and an annual sales volume of around 15 billion euros by 2026. This all confirms that master data management has reached the top of the IT agenda in many companies.
This is only to be expected, because data-driven business models in times of digitalization rely primarily on functioning master data management. The structured maintenance of master data relating to objects such as customers, products, financial transactions, suppliers and business partners is becoming the core task of companies. On the one hand, this is a logical consequence of the digital transformation that has occurred in almost every industry. On the other hand, optimizing SAP master data is a prerequisite for the digitalization of business processes.
How to optimize your material master data – Step by step to a successful project
In this white paper you will learn how to start a project to optimize your material master data in SAP and thus create a solid basis for your future business success.
Avoid High Costs Due to Incorrect Master Data
Effective master data management in companies has the task of providing business processes and SAP transactions with consistent and correct master data. The follow-up costs of having incorrect master data are enormous. This is because a great deal of effort is required to repair the SAP system once outdated or redundant data has flowed into it. This extra labor can be completely avoided with an MDM process that has been optimized from the outset.
Master data management in SAP is anything but a trivial matter. A material master data record in SAP MM alone contains up to 1,000 individual fields.
The single source of truth describes a universal database in the company. If there is no overview, and employees from various departments maintain the data differently, there may, for example, be duplications. The master data will not be reliable and may be out-of-date.
Incorrect master data has catastrophic consequences, particularly in logistics and production processes. Duplicates and unmaintained master data in SAP can lead to incorrect deliveries and material bottlenecks, which in turn can cause considerable disruptions to your business processes in materials management. Your employees must ultimately use manual workarounds to minimize the repercussions so that customer satisfaction is not threatened and follow-up costs are kept to a minimum.
Master data management in SAP is anything but a trivial matter. A material master data record in SAP MM alone contains up to 1,000 individual fields. Maintaining and continuously optimizing SAP master data thus requires the establishment of comprehensive SAP master data governance and the implementation of a predominantly automatic workflow.
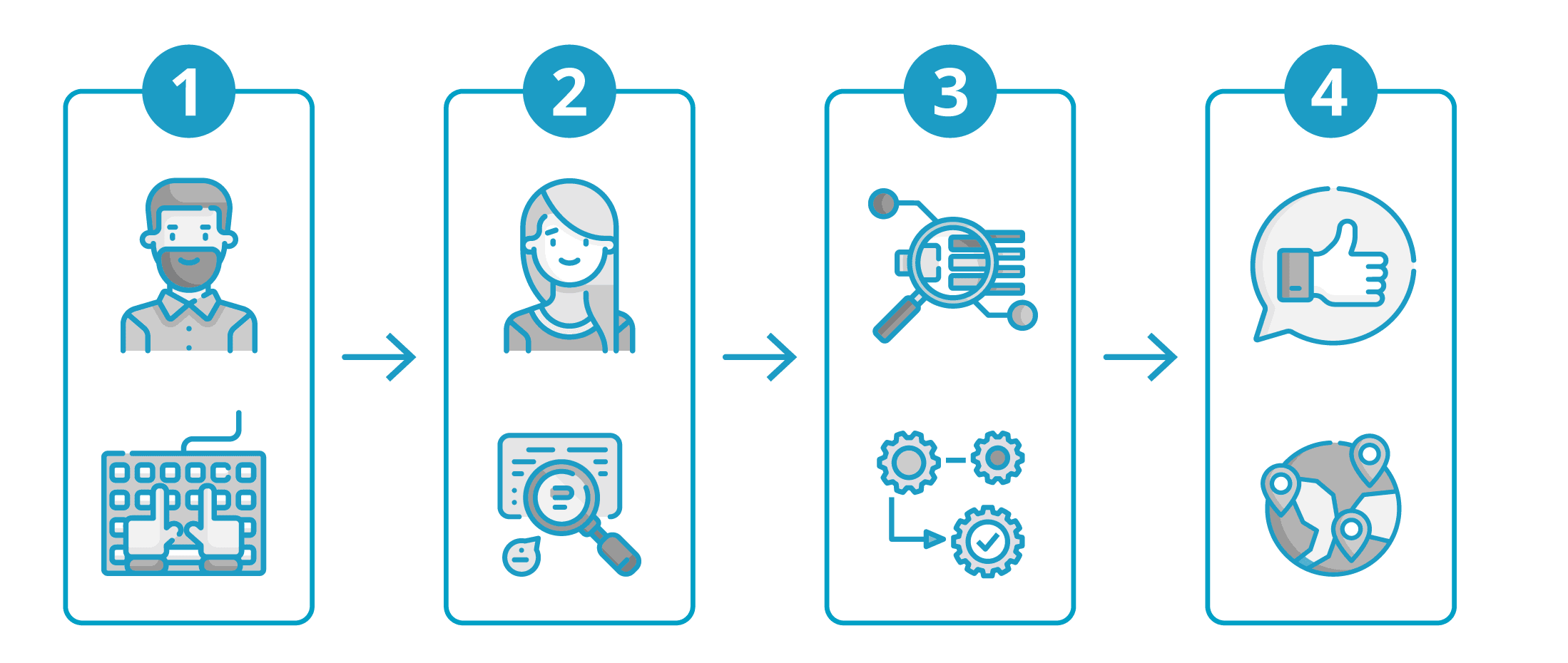
From applying for new materials to optimizing SAP master data across plants, companies can reap the benefits of a structured four-step process. This process has proven its worth, especially for MDM tasks in logistics and production:
- Step 1 – Master data creation when requesting new materials: If an engineer needs a new material, they enter the basic master data directly into an SAP input screen tailored to their role. With the help of the SAP material master views, non-relevant fields are not even displayed, which helps to avoid errors when the material is being created. If required, additional documents and specifications can be attached to the request.
- Step 2 – Release into the master data center: A central department in your organization is responsible for checking and releasing newly created master data records in SAP. This SAP master data center receives new requests via an automated workflow – it checks this and, if necessary, returns it back to the applicant if the initial data record contains errors.
- Step 3 – Check for master data redundancies: SAP applications can be checked for duplicates with the help of digital add-on solutions. If there is suspected redundant master data, the solution will notify your SAP master data center of this. Your employees can then complete the check and update the incorrect master data record.
- Step 4 – Global SAP master data governance: One of the biggest challenges in master data maintenance is the cross-site MDM in distributed organizations. While some data fields are globally valid, others differ from plant to plant. Thanks to special solutions, different plant views can be defined and the solution will automatically create the relevant views for the defined plants.
By linking such a four-level MDM workflow with your SAP system, you can ensure that the risks and follow-up costs resulting from incorrect master data are kept to a minimum. Particularly in times of digitalization, master data management is becoming the supreme discipline for companies that rely on the automation of logistics and production processes.
Problems in material master data management in SAP
Consider this example: An international industrial company manufactures blast furnaces. In order for the equipment manufacturer to be able to work on site, they need a lot of materials – from huge steel parts to single screws – which need to be at the construction site on time. The engineers not only design the gigantic industrial facilities, they also enter the necessary material in the SAP MM. But many of them don’t pay attention to the fact that cross-plant material data help to avoid redundant master data, so that the company benefits from favorable purchasing conditions. They also aren’t interested in the plant-specific material views such as Purchasing and Scheduling, although those views contain important control parameters for the timely delivery of materials to the construction site. The engineers’ attitude is understandable, because they sometimes need thousands of new materials.
The three most common mistakes:
- A material master is created several times, leading to incorrect calculation values.
- The material master creation process is not transparent.
- Production is delayed.
Just the coordination of the departments involved, which maintain their material view, requires an extreme effort. Reducing the entry errors is also complex. All of that drives up the company’s costs. In the worst case, the wrong material is delivered, which not only delays the completion date, but can cost the company millions if, for example, a custom product is involved.
Material Management 4.0 – with clean material master data for digital production
Read our whitepaper to learn all you need to know about the material management challenges and how you can remove the biggest stumbling blocks with digital tools.
Master Data as the Building Block of Digital Enterprises
Master data is basic information about all operationally relevant objects such as customers, suppliers, employees and products. All other data in the company can only be used in a meaningful manner if it is linked to the correct master data. We have learned from experience that unclean master data is one of the primary reasons why digitalization initiatives fail.
Now let’s assume that your master data is completely error-free. What possibilities does it offer? And how can you improve your master data if it needs to be optimized?
What Does Clean Master Data Enable?
While incorrect master data can cause considerable damage, we want to concentrate here on the opportunities that clean master data opens up. Your company can benefit from these four perspectives.
Get the most out of your SAP system
An ERP system such as SAP is by no means an insignificant investment for any company. Most organizations hope to create improved processes and achieve a considerable ROI. Unfortunately, this is often not realized because companies do not fully exploit the possibilities afforded by the SAP system.
Although there are many opportunities for automation, a great deal is still done manually. Processes are far from seamless. One reason for this is that the necessary data is either not available at all or is incorrect – and employees have to bridge this gap with what can sometimes be substantial manual effort.
Your SAP system can only work as well as the existing data basis allows it to. To achieve the full potential and the expected ROI, you need error-free master data.
Automate business processes and decisions
Imagine if your processes could run more or less themselves. The Internet of Things constantly provides data that analytics tools can evaluate. Artificial intelligence uses this data to make decisions and initiate the right processes.
All this can happen automatically without much human intervention. This way, you can bid farewell to gut decisions, as everything is based on data and is one hundred percent comprehensible.
Wouldn’t this free up enormous capacities among your employees? They could then devote themselves to other activities, such as optimizing the system or working on new innovations and business models.
Use analytics and artificial intelligence
It goes without saying that the vast amounts of collected data do not exist as an end in themselves. In order to use it meaningfully, businesses are taking advantage of analytics tools and artificial intelligence.
These can, for example, provide valuable insights into the behavior of your customers, which allows you to predict sales figures as well as calculate material requirements and completion dates. You also gain insights into which parts of the service customers are not satisfied with and can act accordingly.
All this only works if the underlying data is correct. If it is incorrect, the tools will generate inaccurate results and predictions. These are then used as the basis for decisions that will most likely turn out to be wrong.
Exploit the benefits of the Internet of Things
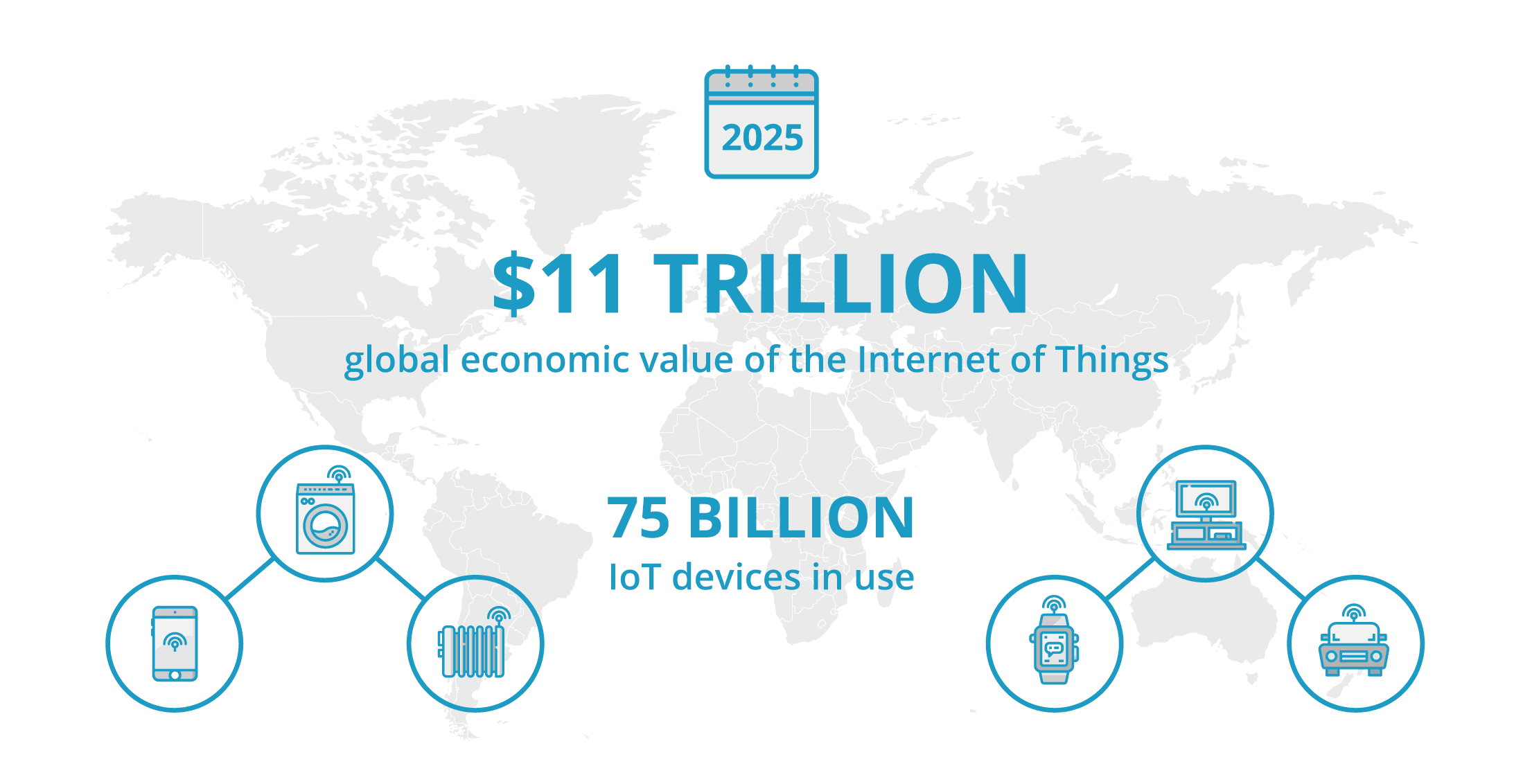
75 billion connected devices are expected to be in circulation by 2025. With the help of sensors, these devices are already exchanging data on a permanent basis, thus merging the physical and digital worlds. For companies, this data opens up a wide range of possibilities for automating and improving their processes while saving precious time and money.
Production example: Machines constantly transmit their workload. If this data is evaluated, recommendations for a more efficient utilization of their capacities can be derived.
Cleaning service example: Sensors transmit the number of people on different floors of buildings. The system uses this data to create a cleaning plan based on the degree of utilization.
The possibilities for using this data are almost endless. However, the Internet of Things can only generate real added value if the received data is linked to the existing master data.
Common Problems with Master Data
Unfortunately, the quality of master data still represents a major obstacle for many companies when it comes to implementing digitalization initiatives. Master data is often…
- undetectable,
- scattered in different systems,
- obsolete and useless,
- inconsistent and contradictory,
- stored in an unusable form.
In addition, there is generally no contact person to answer questions. Even a standardized process for creating and maintaining master data is often sought in vain.
Although a study conducted by the Business Application Research Center (BARC) revealed that data quality and master data management have been a priority for decision-makers for several years, initiatives to improve data quality are being launched rather hesitantly. Companies often perceive them to be too overwhelming, costly and unpredictable.
However, it doesn’t have to be this way. Optimizing master data may be easier than you think.
How Does the Optimization of Master Data Work?
The prerequisite for clean, error-free master data is well thought-out master data management in your company. This has the following tasks:
- Establish processes to regularly and automatically check master data for errors and duplicates.
- Regulate internal responsibilities for master data maintenance and specify what all employees involved have to do.
- Implement data governance standards and best practices to ensure high-quality data, security and compliance.
One of the biggest challenges is that ERP applications like SAP do not offer standardized processes for master data maintenance and often overwhelm users due to their complexity. The solution to this is special software, such as Master Data Management. It’s 100% integrated into SAP andbased directly on the SAP Workflow Engine.
A digital add-on solution for master data management ensures transparent processes, improves data quality and reduces administrative effort. Above all, it minimizes costs by shortening the process duration and eliminating errors and indirect process expenses.
There are preconfigured best-practice approaches that can be implemented in the standard system within a few weeks. Our solution usually pays for itself within a year – sometimes even faster.
How to optimize your material master data – Step by step to a successful project
In this white paper you will learn how to start a project to optimize your material master data in SAP and thus create a solid basis for your future business success.
How production benefits from correct master data
The entire production process – from the creation of the material master data and parts lists to purchasing, supply and production, including the complicated coordination between the departments, up to delivery – holds great potential for errors and delays. In short, an engineer only needs to enter a material into SAP multiple times and there are duplicates and with them incorrect calculation values. Companies in the manufacturing industry particularly benefit from a digitization of processes which is as seamless as possible, such as automated material master data creation, thus achieving decisive competitive advantages: adapted replenishment times, optimized lot sizes and minimum order volumes, reliable exchange of information, shorter cycle times and supply chains and thus measurable cost savings.
How to Calculate the ROI When Optimizing Your SAP Master Data Management
Clean SAP master data is worth its weight in gold. Even seemingly minor errors in master data maintenance can have drastic consequences. Let’s take logistics as an example: If the error devil creeps in when a new production material is created, this can lead to incorrect orders that trigger a toxic chain reaction. The wrong goods are delivered, and the replenishment time for the right materials is several weeks. In the worst case, this can result in production downtime.
However, it’s not only errors and their consequential costs that pose one of the major challenges in SAP Master Data Management. The process of creating and maintaining master data itself requires considerable effort. Companies that create several thousand master data records per year will certainly be familiar with the complexity of SAP as well as the time and resources involved.
The good news: There are ways to optimize and automate the master data process. With the right levers and intelligent add-on solutions for SAP, companies can save money in the shortest time possible. But how do you calculate the return on investment (ROI)? What factors drive up the costs of SAP Master Data Management? And what minor adjustments are actually worth making?
With the right levers and intelligent add-on solutions for SAP, companies can save money in the shortest time possible.
We show you how to calculate the ROI when optimizing your Master Data Management in SAP. In our example, we examine the processing of creating material master records. The calculation works in a similar way for the creation of customer master data as well as other master data processes in SAP.
Optimizing SAP® Material Master Data
In this whitepaper we show you how to fill the digital gaps in your SAP system and benefit from more efficiency, transparency and, above all, a fast return on investment.
What Makes Creating Material Master Data so Complex?
Anyone who has ever been involved in the creation of material master data in SAP is well aware of how complex it is:
- A material master data record in SAP MM contains up to 1,000 individual fields.
- For occasional users, the system and maintenance of it is complicated and confusing.
- Numerous departments such as procurement, sales and material planning are all involved in the master data process.
- Ensuring effective coordination and communication between all process participants in SAP MM eats up a lot of time.
- For companies with multiple production sites, numerous plant views increase complexity levels.
In order to make Master Data Management an efficient process, it’s often worth investing in an additional software solution integrated into SAP. There are many advantages to this. For example, the departments within the company that are responsible for creating and maintaining master data will reap the benefits of a seamless process. The IT department remains true to its SAP strategy and the company management fulfills its commitment to transparent data governance.
Basis of ROI Calculation: Ongoing Process Costs
Whether an investment in a SAP add-on solution for Master Data Management is worthwhile and how quickly you can achieve a full return on investment depends on the following factors:
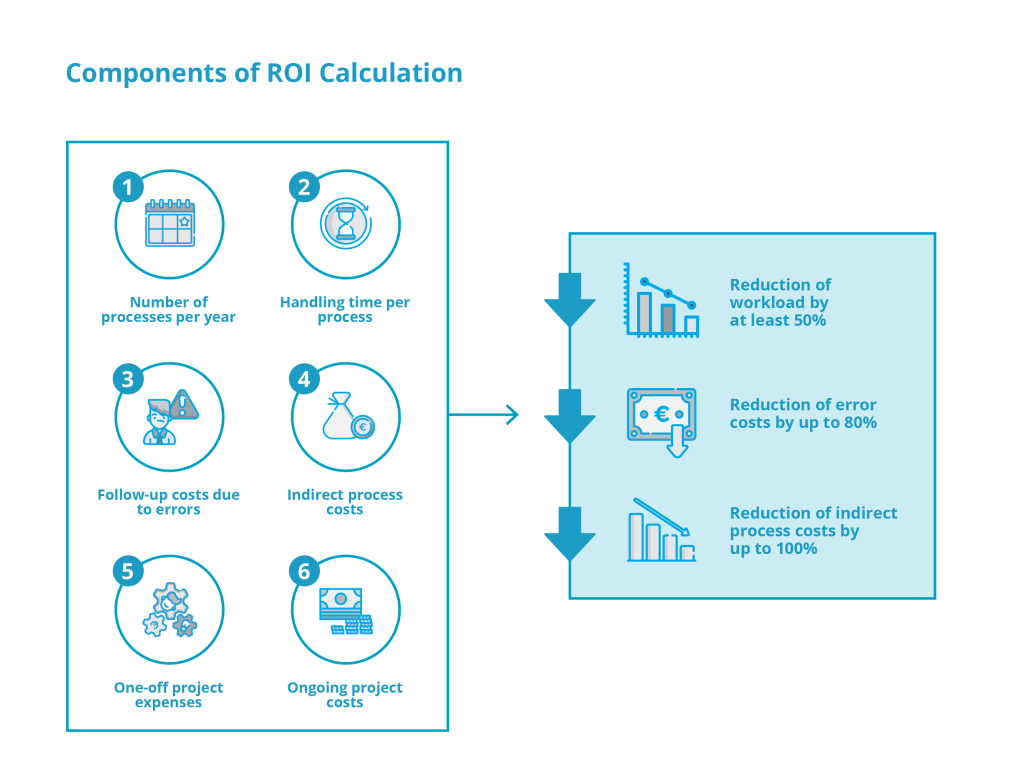
1. Number of processes per year
In a manufacturing company, new materials are requested on a daily basis and created in the SAP system once they’ve been released. The number of material master records created within a year is therefore a decisive influencing factor in determining the total effort required. We estimate that the majority of manufacturing companies create between 1,000 and 15,000 new material master records each year.
Benefit of an SAP add-on solution: No changes, as the number of processes remains the same.
2. Handling time per process
Creating a new material master data record in SAP usually takes between 30 and 45 minutes due to its complexity. Added to this are indirect processing times e.g. telephone queries, the processing of paper-based documents or searching for information in emails.
Benefit of an SAP add-on solution: By optimizing and automating process steps, the workload is reduced by at least 50 percent.
3. Follow-up costs due to errors
In addition to the workload, the follow-up costs resulting from processing errors and duplicates in the SAP material master data are the biggest ROI levers. According to our estimates, the average error costs in the process are around 30 euros per process. This estimate is based on the costs for incorrect material orders and production downtime within one year, divided by the number of processes per year.
Benefit of an SAP add-on solution: Better workflow support and data validation can reduce error costs by up to 80 percent.
4. Indirect process costs
Although the effort and time required is the biggest cost driver when creating and maintaining master data, indirect process costs can also increase expenses. Above all, analog, paper-based processing incurs costs for folders, files, paper, printers, scanners and storage space for documents. The majority of companies have largely digitalized their document management. According to Bitkom Digital Office Index, however, a quarter of companies still work with paper documents.
Benefit of an SAP add-on solution: By digitalizing the analog and paper-based work steps, indirect process costs can be reduced by up to 100 percent.
The Second Part of the ROI Calculation: Project Expenses
The first step of your ROI calculation is complete! You have quantified your current process costs for creating material master data in SAP MM and have compared these with the optimization potential that could be achieved by having a SAP add-on solution.
The second step is to quantify the project expenses. These are broken down into the one-off expenses associated with implementing an SAP add-on solution and the costs for the ongoing operation of the solution.
5. One-off project expenses
The implementation costs consist of the license fees for the SAP add-on solution and the amount of work required to implement it. To find out how much license fees are, we recommend that you contact a specialized software vendor.
In addition, there is the workload for implementation as well as internal project tasks within this framework. As a rule, the more familiar the software vendor is with the selected SAP add-on solution, the faster the implementation will be. Thus, easy software consultants usually need 30 days on site for the implementation, including the recording of the processes and implementation. A consultant first selects a sub-process and examines it using tried and tested checklists. This creates a decisive financial added value for the company. In addition, the SAP development effort is reduced to a minimum: 80 percent of the requirements can be implemented through configuration.
Depending on the complexity of the project, internal project work can take up to 200 days. In your ROI calculation, multiply the estimated project days by an imputed daily rate for external consultants and your own employees.
6. Ongoing project costs
In addition to the initial costs for software implementation, annual maintenance fees are incurred from the first year, which generally amounts to 20 percent of the license costs. In addition, there are labor costs for around 10 days per year – these are for adjustments and configurations, user training when introducing new functions and the implementation of updates.
Short Implementation Time – Fast Return on Investment
Based on these six factors, you can now calculate the return on investment when optimizing your SAP Master Data Management. Our experience gained from numerous ROI studies has shown that project costs pay for themselves in full within one to two years – in many cases it’s even faster.
The following factors in particular lead to an even faster ROI:
- Many master data creation processes and updates
- Lots of manufacturing sites with plant-specific material master views
- Long throughput times and high manual coordination effort
- High follow-up costs for incorrect data and duplicates
Why you should push digitization forward
For production companies, extensive usage scenarios regarding automated controls and even automated corrections are possible. Data evaluations of setup times, production times, wait times and maturing time, but also of material consumption and minimum stocks are possible.
In summary, sophisticated master data management leads to better data-based decisions and ultimately to company growth.
Why the Internet of Things Will Challenge SAP Master Data Management
Increasing connectivity leads to rising levels of complexity in SAP master data management. The Internet of Things is moving into all areas of our lives.
Master data management is a complex issue. Many companies that have continuously invested in their SAP systems over the years are now discovering that not all processes run seamlessly. Problems arise because supposedly automated workflows grind to a halt. One of the underlying reasons for this is bad master data, which makes it impossible to have smooth processes due to incorrect entries or duplicates.
Master data is an essential component of all SAP-based processes in companies. Without clean master data, there is no digitalisation of business processes – and without digitalisation, there is no automation! If you want to make optimal use of your SAP investments, you should urgently redirect your focus to master data management (MDM). In operational practice, however, maintaining SAP master data is anything but simple.
Without clean master data, there is no digitalisation of business processes – and without digitalisation, there is no automation!
For example, a material master data record in SAP MM contains up to 600 individual fields. In fact, up to a dozen departments of a company could be involved in maintaining these fields. In global companies, geographically dispersed production sites and confusing organisational structures are added to the equation – perfect recipe for chaos! How do companies bring this complexity under control?
The good news: There are a number of tried and tested digital solutions for master data management. However, we will not be dealing with that topic in this blog post. Instead, we will look at why everything will become even more complex in the future!
Universal Connectivity Leads to Exponential Data Growth
Increasing connectivity is the main contributing factor to rising levels of complexity in SAP master data management. It’s a fact: The Internet of Things (IoT) is moving into all areas of our lives. With the help of connected sensors, the physical and digital worlds merge and weave into a digitally integrated ecosystem.
On the one hand, this is made possible by rapidly falling sensor prices, which have halved in a very short time. On the other hand, with 5G we have a new mobile radio standard just around the corner that was developed to ensure universal connectivity and to enable “always on” at high speed. McKinsey puts the macroeconomic value of the Internet of Things at up to 11 trillion dollars per year. With more than 75 billion connected devices by 2025, the IoT will touch every facet of our lives.
It goes without saying that the Internet of Things is also making its way into companies. Connected production processes (keyword: Industry 4.0) have long since become a reality, even if many organisations are only at a tentative first stage of expansion. The new technical possibilities afforded by IoT enable companies to rethink business processes. “We’ll do truly different things, instead of just doing things differently,” says Daniel Wellers of SAP, in a very readable article for the World Economic Forum.
The Internet of Things holds many new challenges in store for master data management. We get a rough idea of the issues facing data management when we consider that as IoT connectivity grows, the amount of data generated worldwide will double over the next decade.
We looked at three scenarios that give us a decent idea of how the Internet of Things will challenge master data management with SAP.
Data Explosion Overloads Manual MDM
One of the greatest challenges in master data management today lies in the company-wide amalgamation of different data sources. Companies using SAP manage their material master data in SAP MM. To add to this, there is a CRM system for customer data and potentially two to three other systems. Business processes can only seamlessly use master data if it is cleanly maintained.
Master data management meets this need by identifying gaps and triggering a workflow to correct the problem. These corrections are usually carried out manually by a dedicated team. With growing IoT connectivity along the entire value chain, the volume of data is growing exponentially. Manual processes to improve data quality are likely to quickly reach their limits because the flood of data will exceed the processing capacity.
Semantic Challenges in the Flood of Data
The Internet of Things only provides added value for a company if it can establish the connection between the data generated from the network and the material master data. For example, a production machine could share utilisation data with another machine. In the event of peaks in production, both machines could send the production manager a request to improve capacity utilisation.
Such an application example requires that the semantic context for the master data and the sensory IoT data is defined. For example, if a sensor with the tag “ABCDE12345” supplies the information “123.456.789”, valuable information will only emerge from the reference to the master data. Given the enormous number of sensors and event types to be expected, companies are faced with an exciting semantic challenge.
Can MDM Also Handle Master Big Data Management?
Until now, master data management solutions have not been designed for Big Data. Individual data records are complex in themselves. With regard to the number of data records, most companies operate in dimensions of several tens of thousands, as is the case in materials management.
The Internet of Things is triggering the exponential growth of the volume of data. Complex analyses only create real added value if they relate existing master data to newly created IoT data points. It seems that many of the current database concepts may not be designed for this. Statistical evaluations can be created, particularly when based on relational database technologies. However, reliable forecasts such as the expected demand behaviour of customers or the predicted downtime of production machines cannot yet be generated.
There is still plenty to be getting on with! With the deeper integration of the Internet of Things into business processes, data will become an even more decisive competitive factor than it was previously. Now is the ideal time to get rid of your master data management before IoT connectivity makes matters even more complicated. So what are you waiting for? Get the ball rolling now!
The solution: Maintain material master data with SAP integration
What does sensible material master data maintenance require, and who in the company benefits from it? The departments which enter their needed materials are interested in a fast, smooth process that is as simple as possible. The IT manager wants complete integration in SAP in order to avoid additional training. And the management wants comprehensive overview in order to minimize cycle times and resource costs and increase data governance.
Individual and intuitive interfaces
The software solution for material management runs directly in SAP and uses the SAP business workflow to eliminate the manual coordination effort. The system builders use the process conveniently via a web interface based on SAP Web Dynpro. They can thus easily apply for material from anywhere and enter the basic data. The departments such as purchasing, materials planning, sales and accounting then maintain their views. The crux: The user interface can be individually adapted to the needs of the respective department without having to program Web Dynpro. The process flow can also be easily adapted to customer requirements in the respective project.
Duplicate check
EASY Material Management for SAP Solutions helps the facility builder to avoid redundant data. It allows employees to check if an ordered material already exists in SAP. The duplicate check relies on the material description and drawing number and can be expanded with additional parameters within the project.
Validation of the material master data
As a result of EASY Material Management operating directly in SAP, all SAP search help and validation tables can be used directly. Thus, users can only select values in the material master data creation process which are also provided in the SAP System.
Plant copies
The material data are usually used in more than one plant and therefore need to be maintained for all sites. In many cases, this manual maintenance can be automated if the entry data are identical.
360° view of your material master data
With SAP integrations like easy Material Management, departments have easy and individual interfaces available to coordinate the process flow. Scarce personnel resources are free for other tasks and the error rate is reduced. Since no additional hardware is necessary and the software solution operates in SAP, that takes some pressure off of IT. Finally, management achieves 360° process transparency to reduce cycle times and maximize optimization potentials. In addition, most of the expenses for the previously manual process coordination no longer apply.
Process transparency in particular comes in very handy in the Sales department to show customers that the company is in command of its order processing. Wouldn’t it be great if you could tell your customers that you are completely in charge of your processes?
Webinar: EASY Material Management – Change and create master data
You have recognized that clean material master data leads to success in your company? Now it’ s time to move on to the next steps: The selection of a suitable service provider for the digitalization of your material master creation process.
Master Data Management in SAP and the Migration to SAP S/4HANA
Functioning master data is one of the most decisive factors influencing the success of digitalization initiatives in an organization. In this context, companies cannot avoid dealing with another transformation: the introduction of SAP S/4HANA. Although it’s true that SAP has extended maintenance of the old SAP Suite until 2027, the migration will finally come and, in our experience, will also generate great added value for companies – provided it is approached correctly.
In this blog post, you’ll discover what companies need to pay attention to when dealing with master data in light of the upcoming migration to S/4HANA, what changes SAP S/4HANA will bring for master data and what options are available when migrating to S/4HANA.
Master Data Management Poses a Permanent Challenge
Although data quality and master data management are at the top of the priority list for decision-makers in many companies, master data management is often neglected. On the one hand, this is because master data isn’t handled in day-to-day operations. On the other hand, the topic appears so complex at first glance that problems are suppressed for as long as possible.
However, the consequences of inadequate master data management are sometimes rather severe. Incorrect material master data can quickly lead to incorrect planning in a company, resulting in delivery bottlenecks or other financial consequences. The sticking point in master data management is relatively easy to identify: the creation of material master data in SAP. There are several reasons for this:
- Entering data into the SAP system is incredibly error-prone. The problem often lies in the cooperation between people and technology. For example, it’s easy to overlook errors when entering data, materials could be created twice or employees are simply not aware of the complexity of the data records because they rarely use the system.
- If errors are discovered, it requires significantly more coordination involving conversations, emails and calls to fix the incorrectly created material data.
- Even correctly created material master data can delay downstream processes due to complex approval procedures.
- If a process comes to a standstill because a process step has stalled somewhere in the system, it’s often difficult for those involved to see exactly where the problem lies and how to solve it.
What Requirements Master Data Management in SAP Must Fulfill
Organizations have to meet the challenges of master data management with a clean process for creating the material master in SAP. It often makes more sense to completely restructure the entire material master creation process rather than trying to patch up a bad process in various places. Businesses don’t have to reinvent the wheel for this, as they can fall back on tried and tested practices that reliably lead to success.
In essence, this is about setting up a process with which you can create the material master in SAP and change it if necessary. In addition, you should set goals on how to optimize master data management as a whole. The following considerations may play a role in this. The creation of master data should:
- Be flexible enough to accommodate material types and other specific requirements,
- Run as automated as possible in order to save resources and minimize errors,
- Increase lead times to accelerate downstream processes,
- Be so transparent that it’s immediately obvious when and at what point a process has stalled and who’s responsible for it.
What the Introduction of S/4HANA Means for Master Data Management
Migrating to S/4HANA offers users a number of advantages in terms of master data management. Overall, the new database software is more efficient and cost-effective to operate and opens up new use cases for companies. The biggest benefit that is immediately noticeable for users is that S/4HANA performs much better in the background than its predecessor, SAP Business Suite 7. The biggest tangible change of S/4HANA is that SAP delivers the software with the newly designed user interface SAP Fiori, for which there’s also an application on mobile devices.
Furthermore, there’s an important development that has a direct influence on master data management, namely the basic distinction between “debtor” and “creditor” is no longer made when creating customer or supplier data. Instead, customers and suppliers are always created and maintained in S/4HANA as “business partners”. This has the advantage that the same master data record can be used for a business partner who is both a customer and a supplier. Different roles can be assigned to a business partner, for example as “debtor” and “creditor”.
In addition, there are other minor changes in S/4HANA that also affect master data management. For example, several currencies can now finally be stored and the material number field can be expanded to up to 40 characters. It’s also important to note that individually developed solutions from the old SAP Suite, known as Z programs, may no longer function properly after migration to S/4HANA.
How Companies Can Shape Their Migration to S/4HANA
When migrating to S/4HANA, companies can choose between three paths. The reason for these choices is that SAP offers its customers different operating models for S/4HANA. These are:
- The cloud solutions SAP S/4HANA Cloud Essential Edition (ES) and SAP S/4HANA Cloud Extended Edition (EX)
- The server-based versions SAP S/4HANA On-Premise managed by SAP (HEC) and SAP S/4HANA On-Premise.
Besides the cost aspect and update management, these four S/4HANA solutions differ mainly in terms of flexibility: while the Essential Edition is the most standardized, the On-Premise version offers companies the greatest flexibility in terms of set-up.
What does this mean for migration to S/4HANA? While the SAP S/4HANA Cloud Essential Edition (ES) can only be migrated with a greenfield project approach, companies can choose between a greenfield, brownfield and bluefield approach for the other versions. In practice, this means the following for master data management:
- When migrating the SAP system according to the greenfield approach, you lose your old data and have to recreate it all. In this regard, businesses must assess whether this opportunity to restart with the option of completely rebuilding many processes outweighs the cost of losing the old data when migrating to the new system.
- The brownfield approach is the opposite of the greenfield approach, since all historical data is kept and migrated completely into the new system. To do this, you have to ensure in advance whether the existing master data is really suitable for this step or must be cleaned up beforehand if necessary. The benefit of this approach is that it gives companies the opportunity to migrate the ERP system to SAP S/4HANA very quickly with all historical data and still be able to make the most of the new system.
- The bluefield approach is a mix of greenfield and brownfield: the historical data is transferred selectively and the new system is rolled out in the company in several go-live phases, which helps to reduce project runtimes under certain conditions.
Webinar: Your migration to SAP® S/4HANA
Have you already decided to migrate to the new version S/4HANA? Then it’s time to plan your project approach. In our webinar recording, you can discover which project strategy will ensure your migration is a success – request the recording free of charge now.
When you decide to switch to SAP S/4HANA, you are faced with the challenge of having to migrate your data to the new system. This is your chance to clean up and start with clean master data from the beginning! Clean customer master data are essential in order to be able to process customer orders quickly and efficiently. Only then can customer orders be handled smoothly across all markets and channels. Satisfied customers are the “cherry on top”.
When you handle customer orders, you rely on customer master data in a variety of process steps – from the customer query to the availability check and delivery and on to payment.
The challenges in the manual creation of customer master data
In practice, new customer master data often come through “chaotic” processes in SAP® SD (Sales and Distribution), because the necessary information is rarely bundled, but rather usually present in emails and caller records. Therefore, errors can result from the manual transmission of the data to the SAP® system. In addition, the time and expertise to check if existing customer data can be used or updated are frequently lacking. Instead, employees often create redundant master data. The effort of providing customer master data to the necessary sales areas and company codes should also not be underestimated.
An optimized creation process works this easily
- Customer data record: A field service employee would like to record a new opportunity and needs a new customer to do so. They enter the basic data and perform a duplicate check.
- Enriching the customer master data: A field service employee would like to record a new opportunity and needs a new customer to do so. They enter the basic data and perform a duplicate check.
- Check data quality: In order to increase the data quality, a sales inspection team can double-check the entries before the new customer master data is actually automatically entered in SAP®.
- Company code: In order to increase the data quality, a sales inspection team can double-check the entries before the new customer master data is actually automatically entered in SAP®.
- Credit rating and dunning: Credit rating, sanction lists, and dunning can be optionally integrated.
- Data creation in SAP: Credit rating, sanction lists, and dunning can be optionally integrated.
Optimize SAP® master data
In this white paper you will learn how to start a project to optimize your material master data in SAP and thus create a solid basis for your future business success.
Data migration to SAP S/4HANA
Those who decide to implement SAP S/HANA face a challenge: Each program or version change of a software package is associated with the fact that the master data of a database also has to be exported correctly from the old system and imported into the new system, which therefore includes the material master data. When migrating to SAP S/4HANA, the migration of the master data is associated with particular challenges, as SAP has changed the tables and/or structures for certain master data objects.
Therefore, data migration is a task that cannot be underestimated. After all, depending on the type and size of the company, the amount of data records can be considerable. These records are also the basis for a large part of the business processes. It is therefore necessary to ensure that the data migration is error-free and complete.
At the same time, however, this task also offers the opportunity to optimize the data quality and to streamline processes so that they can work efficiently with the new system right from the start. After all, it is frequently the case that material master data in particular and master data in general aren’t managed flawlessly. The goal should be to get rid of legacy data in advance, and to only transfer correct, complete and redundancy-free data. This can also have a positive impact on the migration work, as the more obsolete material master data you transfer to SAP S/4 HANA, the more costs and resources you require for the migration. It is estimated that poor data quality causes approximately 40% of the total migration project to cost more in terms of both the timescale and budget.
In this respect, a certain amount of preparatory work is required. In the following, we present the four steps of the successful migration of master data to S/4HANA.
1. Data analysis – know your data!
Before you start optimizing your data, it is essential for you to complete a stock-take. Insufficient knowledge of your own data and processes is one of the most frequent reasons for additional costs and time overruns during migration projects. Make sure that you gain an overview of the quantity and quality of your material master data, as this is the only way to correctly estimate the total migration outlay. You should therefore complete a critical check of which data you actually still require. You may have data that is no longer valid or that will no longer be actively used in the new system. If you look at the business processes, it should rapidly become clear what else is relevant. This is an opportunity to get rid of unnecessary ballast, and to keep the new system clear of old burdens right from the start. Therefore, instead of migrating everything, material master data that is no longer required can be archived, for example, if it cannot be erased due to legal requirements.
Duplicates are a frequent source of errors in material master data. In this context, it is necessary to define when data records are considered duplicates. How do I manage two data records that are basically identical, but differ in terms of the spelling of the material description, for instance? Therefore, to identify duplicates, it is necessary to determine the degree to which two records must match in order to be considered duplicates. This can be done on the basis of the material designation, manufacturer part number or both parameters taken together, for example. It is also important to search for fragments of the material designation, as this is the only way to ensure that similar designations are identified. It is also a good idea to shed light on the reasons why duplicates occur. If too many employees have write access to the database, this can encourage the creation of duplicate data. Defining exactly who actually needs access and who should have what level of authorization is therefore worthwhile.
Incomplete data is another common problem. Moreover, data fields are often not maintained consistently. For example, there may be discrepancies in the spelling of country codes, which are sometimes entered as single digits and sometimes as multiple digits. Also, fields are often not used for their intended purpose, but for entering different information. This creates an inconsistent data source that can cause problems with your master data management. For these fields, it is necessary to define which contents are allowed and in which format, and to therefore avoid these problems.
Another point to consider in your analysis is the differences between legacy systems and new systems. As mentioned at the outset, SAP S/4HANA brings in a number of changes. There may be process changes, or the length of the input fields may differ, so that content may possibly be truncated during the migration. These discrepancies and possible solutions should also form part of your analysis.
2. Data cleansing – the basis for a clean start in SAP S/4HANA
Once you have a picture of the quantity and quality of your data, it is time to take the next step on the path to data migration to SAP S/4HANA: cleansing the material master data. In addition to erasing data records that are no longer required, such as duplicates, it is also important to supplement and complete incomplete data records, as only then can you work efficiently with them.
A crucial question is how to carry out the cleansing and data enrichment. This can, of course, be completely manually, but this has the major disadvantage that it is extremely time-consuming. Alternatively, there are ways to automate the cleansing process. However, as this is not entirely without risk, it is often advisable to use a service provider. After all, important data can be lost if the procedure is not carried out correctly.
3. Migration of data to SAP S/4HANA – efficient and coordinated
After the groundwork has been done, the time has finally arrived: Your material master data can now be migrated to the new system. By checking and cleansing the data to be transferred beforehand, old and incorrect data is excluded, and you only transfer high-quality and relevant master data. Here, too, it should be checked in advance exactly how the data can be transferred to the new system and which tools and auxiliary products come into question.
Once the data migration is complete, it is essential to check whether all the data has been transferred completely and correctly. In this way, you guarantee high quality master data as the basis for your business processes.
4. Have confidence in your data!
You’ve done it! Your master data has been successfully migrated to SAP S/4HANA, and you can now make a fresh start with a clean database without legacy data.
A well-planned changeover with cleansed data has several positive developments. These include, for example:
- Improved performance of SAP S/4HANA
- Optimized business processes
- Reduction of duplicates
- Less disk space required after cleanup
- Easy administration of the database
- Lower running costs for space in the main memory
- Fewer resources for the changeover and reduced overall operating costs
Your hard work and advance planning has therefore paid off. To prevent its benefits from fizzling out, however, it is advisable to ensure that the data quality remains consistently high. Even if it seems arduous: take time to complete a regular quality check. Have duplicates crept in again? Are any data records incomplete or incorrect? This not only affects the material master data. Remember that all master data (e.g. vendor or customer master data) can change regularly, due to relocations or changes in company name, for instance.
The time that you spend on quality control and maintenance of your material master data is therefore well invested if you want to work with it to optimum effect.
The Importance of Company-Wide Master Data Governance for SAP Users
Companies are processing ever increasing amounts of data from a wide variety of sources (keyword: Internet of Things). The most important type is master data, which contains basic information about customers, suppliers, employees and products. It forms the basis for the digitalization and automation of business processes. Used correctly, businesses can leverage data to better respond to customer requirements and changes in the market.
However, incorrect data can lead to wrong decisions and cause considerable damage. If personal data is not handled in a legally compliant manner, companies could even find themselves in legal difficulties.
This is why organizations today need a strategy for the correct management and processing of master data. Data governance provides the necessary framework for this. In this blog post, you will find an introduction to the topic and learn why no company can afford to do without data governance in times of digital transformation.
What Is Data Governance?
Data governance is the comprehensive handling and management of all data processed in a company. It consists of guidelines and procedures that guarantee the quality, protection and security of data. Furthermore, it is intended to ensure that legal requirements are always met.
However, data governance is not a one-off project that can be implemented and ticked off your to-do list. Rather, it is a continuous process. Depending on the size of the organization, individual people, often called Data Governance Officers or Chief Data Officers or even entire departments are responsible for overseeing the data governance.
Data governance ensures that master data in the company are checked for availability, integrity and security, that data management is continually monitored and that processes for higher data quality are implemented – irreplaceable for maintaining high data quality over the long term.
What Does Data Governance Seek to Achieve in Companies?

The primary goal of data governance is to maintain and further enrich internal company knowledge. In addition, the following should be achieved:
- Data quality: All data should always be up to date, complete and readily available.
- Data maintenance: Data must be enriched and corrected if necessary.
- Data protection: Confidential personal data must be protected against unlawful use.
- Data security: Unauthorized access, reading or deletion of data must be prevented.
- Data compliance: Companies must comply with legal requirements as well as internal company and industry standards.
Many companies work with ERP applications that already meet some of these objectives. For example, SAP canregulate who has access to specific master data, preventing unauthorized access. However, SAP’s standard product does not offer a complete solution for data governance.
Why You Can’t Afford to Do Without Data Governance
In times of digital transformation, correct master data is essential to ensure that companies maintain their agility and ability to react to changing circumstances. These four reasons underscore the importance of data governance.
Avoid errors and follow-up costs
We would like to explain the damage that unclean data can cause using the example of material master data. It forms the basis for many essential processes in production and logistics.
To create material master data records correctly in SAP, up to 600 fields must be filled in. Creating and maintaining these data records involves numerous departments and even external stakeholders such as customers and suppliers. Coordinating all the parties involved poses a genuine challenge.
Without a transparent process for creating and maintaining master data, most errors remain undetected, which can lead to serious consequences. For example, if the wrong material is ordered, completion dates can be delayed. This can cause significant economic damage for organizations.
Serves as the basis for the successful digitalization of business processes
To begin with, the status quo of data management in the company must be mapped. You should ask questions like: Who is the owner of the master data? Who manages the master data? And who has access rights? When it comes to material master data, the process of creating and maintaining data records must be examined with particular care.
Work in a legally compliant and secure manner
Special attention should be paid to personal data, such as customer and employee master data. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which lays down the principles for processing personal data, applies within the European Union. Companies must prove compliance with this regulation. If these principles are not implemented in a legally compliant manner, companies can expect penalties of up to 4% of the total annual turnover generated worldwide.
Data volumes and complexity set to increase
The growing connectivity of devices in the Internet of Things provides a continuous stream of data that must be processed in the shortest time possible. Estimates suggest that a whopping 175 zettabytes of data will be available worldwide by 2025, which will only add to the complexity of data management.
Greater connectivity and complexity also means that even minor errors in master data can trigger unexpected chain reactions. Incorrect data therefore poses an even greater risk for companies.
clean material master data for digital production
The digitalization of industrial production is one of the most important projects for the future. Invest today in material management and material master data and create the conditions for digitized production.
The First Steps to Data Governance in a Company
The first challenge is to properly embed data governance into the corporate structure. It must be clear that master data management is not purely an IT task. All departments that work with data are involved. Then, you can follow these three steps.
1. Begin with one area
Depending on the size of the business, implementing a company-wide data governance project can be a mammoth task, especially when there are countless types of data and stakeholders that need to be involved. So where should you start?
We recommend beginning with an area where optimization can have a great impact. For many companies, this is material master data. Once you have gained some initial experience, it will be easier to transfer the data governance standards to other areas.
2. Determine the current status
To begin with, the status quo of data management in the company must be mapped. You should ask questions like: Who is the owner of the master data? Who manages the master data? And who has access rights? When it comes to material master data, the process of creating and maintaining data records must be examined with particular care.
3. Establish data governance processes
The next step is to define processes that describe how your data should be backed up, protected, stored and archived. This includes guidelines on how certain data may be used and which persons or departments are authorized to perform which actions. Furthermore, control processes are required to ensure the continuous monitoring of compliance and adherence to legal requirements.
Digital Solutions Facilitate Data Governance
Master data management is extremely complex, especially in SAP environments, and doesn’t just present a challenge for occasional users. Until now, SAP has not offered a simple, standardized data governance process. However, there are specialized software solutions, such as Master Data Management for SAP, that can assume this role instead.
They ensure transparent processes and enhanced data quality. With an easy-to-use interface, they reduce the administrative workload while automated processes minimize data maintenance work for employees.





